Overview
Origin Documentation
Origin Documentation, also known as proof of origin, helps to attest to the origin of goods. Broadly, there are two types of origin, namely non-preferential origin and preferential origin.
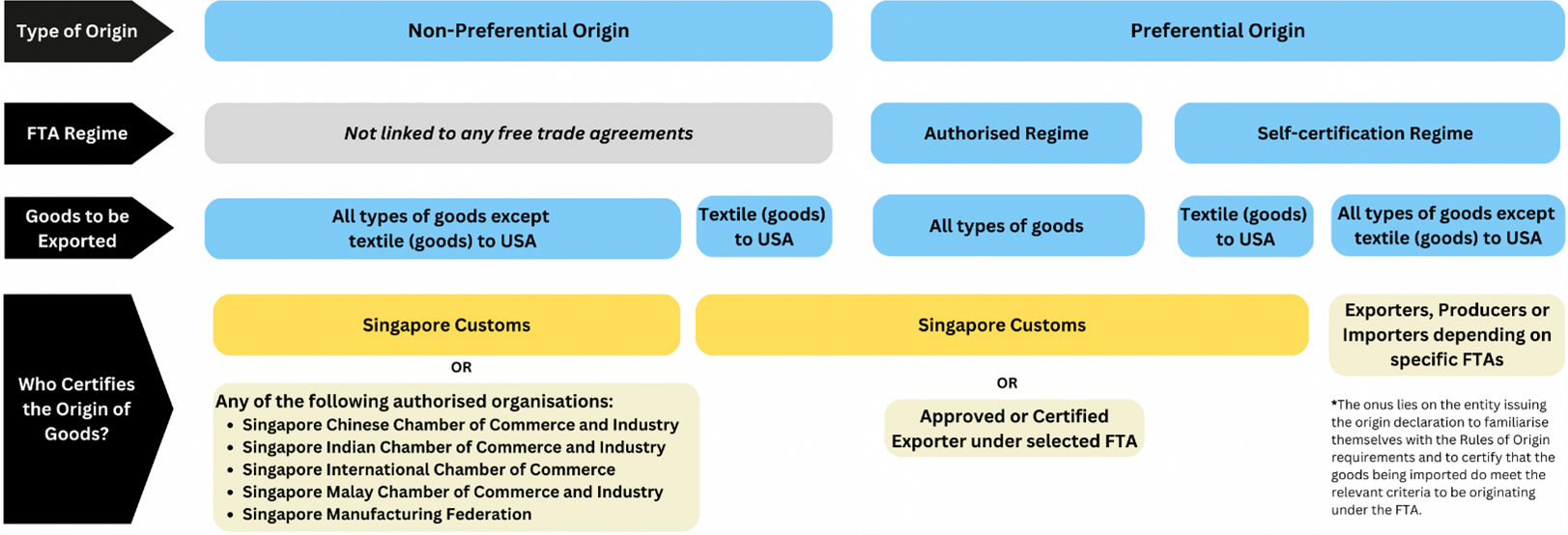
Non-Preferential Origin
An ordinary Certificate of Origin (CO), also known as a non-preferential CO, is a trade document that helps to identify the origin of the good.
You may refer to this handbook for more information on the rules of origin for ordinary COs.
-
Who can issue an Ordinary CO?
Ordinary COs are issued by Singapore Customs or any of the following authorised organisations:
Apart from Singapore Customs, these authorised organisations do also issue ordinary COs for locally manufactured or processed goods, and goods from other countries which are re-exported from Singapore. However, they do not issue ordinary COs for the export of Singapore-origin textiles and textile goods to the United States of America.
-
How to Apply for Ordinary CO?
You may apply for an ordinary CO with any of the five authorised organisation through their website.
To apply for an Ordinary CO with Singapore Customs, you may refer to the following guide on How to apply for OCO or PCO with Singapore Customs
Preferential Origin
A preferential proof of origin allows your buyer to pay lower or no customs duty when you export your goods under a Free Trade Agreement. You may refer to Enterprise Singapore's Tariff Finder Tool to assist you in the following:
-
Whether the goods are covered under Free Trade Agreement and the corresponding preferential tariffs.
-
Which Free Trade Agreement is most suitable for your goods.
-
Who can issue a preferential proof of origin?
The type of preferential proof of origin applicable for your goods depends on the requirements under the specific Free Trade Agreement that you apply for.
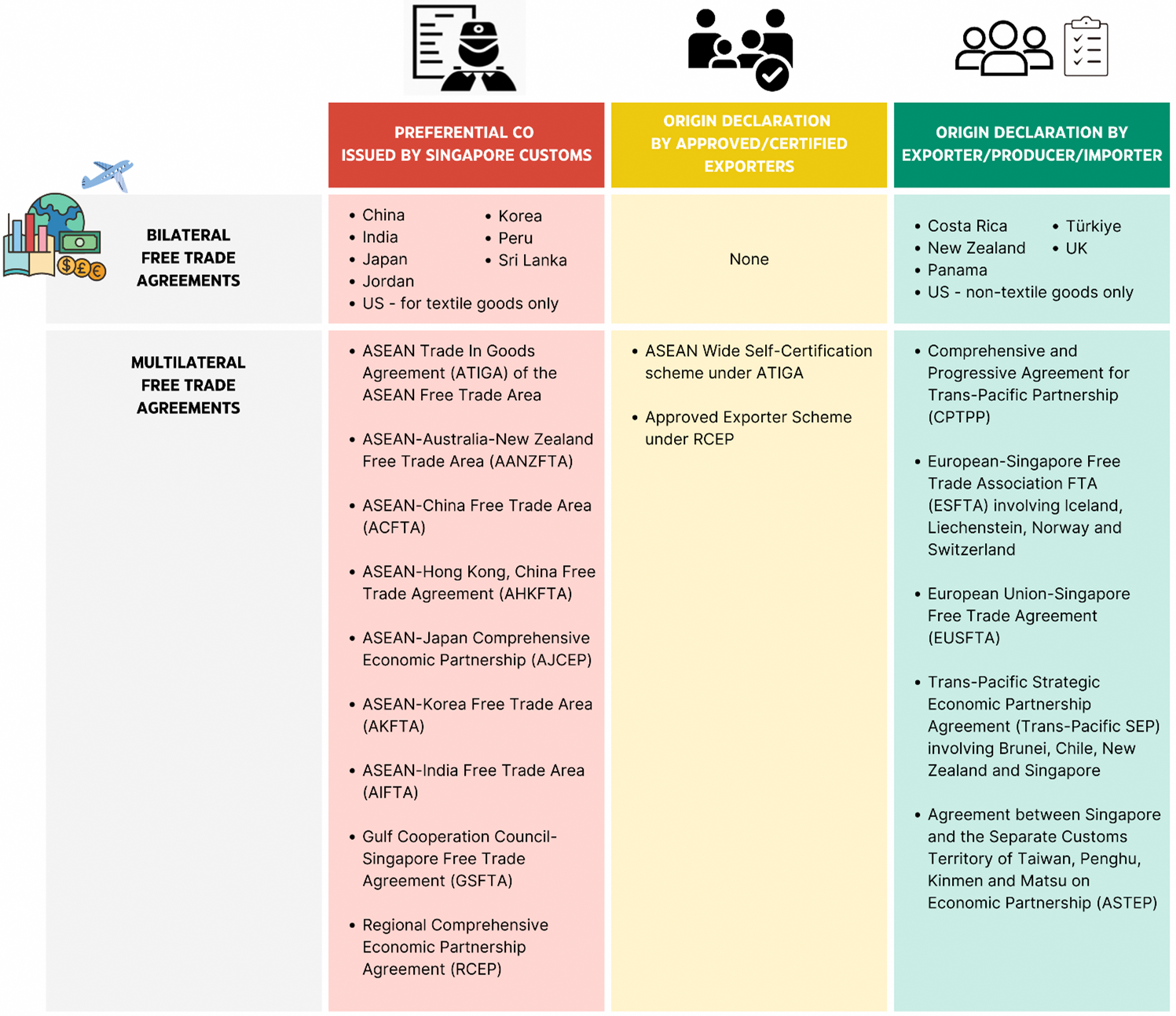
There are three different types of preferential proof of origin:
-
Preferential CO issued by Singapore Customs
-
Origin declaration by Approved/Certified Exporters
-
Origin declaration by Exporter/Producer/Importer
-
-
How to obtain a preferential proof of origin?
Certification by Customs Authority
For Free Trade Agreements that require Certification by Customs Authority, you may refer to the following guide on How to apply for OCO or PCO with Singapore Customs.
You may refer to Handbook on rules of origin for preferential Certificates of Origin for more information on the rules of origin for preferential COs issued under Free Trade Agreements.
You may use the FTA Cost Statement Calculator for a preliminary assessment of the qualifying value content and/or Change in Tariff Classification status of your manufactured good under a specific Free Trade Agreement, after you have identified the applicable origin criterion(a) for the good under the Agreement.
Approved Exporter and/or Certified Exporter Scheme
To find out more about the Approved Exporter and/or Certified Exporter Scheme administered by Singapore Customs, you may refer to the following guide for more information.
Approved Exporter and/or Certified Exporter Scheme
Self-Certification Regime
For Free Trade Agreements that are under the Self-Certification regime, you may refer to the following guide for more information.
For more information on:
Best Practices
You are accountable as an exporter or declaring agent for the export of your goods. We encourage you to take note of the following Dos and Don’ts:
-
Do
✔ Inform Singapore Customs if there is any change in your company’s particulars to ensure you receive timely updates on regulatory changes.
✔ Know the export procedures and declaration requirements before you export.
✔ Ensure you provide the necessary supporting documents and information for permit declarations to your declaring agents and freight forwarders.
✔ Ensure your declaring agents and freight forwarders understand and properly execute your instructions.
✔ Know the contents of each consignment you export and clarify with relevant parties if needed.
✔ Keep your supporting documents for a minimum of 5 years.
✔ Check with the relevant Competent Authority on their requirements to export controlled items.
✔ Ensure product details (for example, HS code, quantity) are correctly declared.
✔ Ensure you comply with all permit conditions stated in the permit.
✔ Ensure your driver or transport service provider produces the permit for endorsement at the checkpoint if the permit bears such a condition.
-
Do Not
✖ Deny Singapore Customs officers’ requests to enter your premises or to check your documents.
✖ Make a declaration without verifying the authenticity of all supporting documents.
✖ Declare that goods are of Singapore origin when they were only imported and re-exported from Singapore without qualifying for their origin status.
✖ Share your TradeNet user ID and password with other persons.
✖ Use your company’s UEN to export goods not belonging to you unless you are involved in taking the goods out of Singapore for export and are willing to declare yourself as the exporter on behalf of the party that issues the export invoice, or you are acting as a consolidator for customers without a UEN. In doing so, you are responsible for complying with all the regulatory requirements. Please refer to Customs Circular No. 13/2021 for more information on the responsibilities of an exporter.
Offences
Companies may be penalised under the Regulation of Imports and Exports Act (RIEA) if they do not comply with requirements relating to rules of origin.
Examples of common offences
-
Making a false declaration
-
Deliberate false declaration of country of origin
-
Declaring non-Singapore origin materials from local suppliers as Singapore-origin
-
-
Incorrect trade descriptions
-
Affixing false labels of origin on textile goods
-
-
Failure to retain documents for the minimum retention period
-
Retaining supporting documents for preferential tariffs claimed under the US-Singapore Free Trade Agreement for 3 years instead of the minimum 5 years
For minor offences under the RIEA, Singapore Customs may offer to compound the offences for a sum not exceeding S$5,000 per offence. Offenders may be prosecuted if the offence committed is of a fraudulent or serious nature.
Penalties upon conviction for key offences
|
Offence |
Penalty Upon Conviction |
|---|---|
|
Making a false declaration.
|
A fine not exceeding S$10,000, or imprisonment not exceeding 2 years,
or both.
|
Learn more about the prescribed offences and penalties under the Customs Act and the RIEA.






