Import Operations Overview
This page provides a quick guide on the import procedures for those who wish to import goods into Singapore.
On this page
Imports
An import refers to goods brought into customs territory from an entry point or a Free Trade Zone (FTZ), or overseas goods brought into a FTZ for storage and pending re-export.
To import goods into Singapore, you are required to make a declaration to Singapore Customs. Goods and Services Tax (GST) is payable on non-dutiable goods. Both GST and duty are payable for dutiable goods if these goods are imported for local consumption.
How to Import Your Goods?
General Import Flow Chart
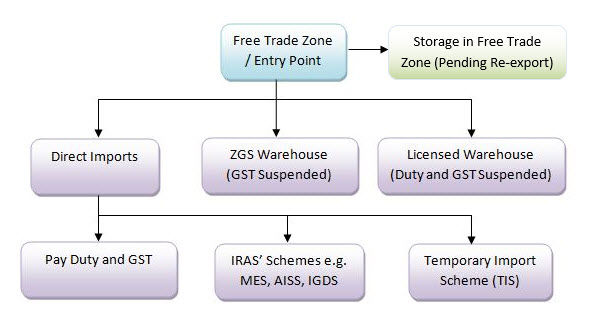
This diagram outlines the procedural options for importing goods, ranging from immediate payment of duties to the use of specialized storage and tax suspension schemes.
As an importer, you will need to first determine if duty and/or GST payment should be made when your goods enter Singapore:
Duty and/or GST are suspended when goods remain inside a FTZ
Duty and/or GST are payable if goods are released directly for local circulation
When goods are moved from a FTZ or entry point into a Customs licensed premises (such as zero-GST warehouses or licensed warehouses), duty and/or GST will be suspended as long as the goods are stored in the licensed premises
Duty and/or GST are not payable for goods granted duty exemption or GST relief or those imported under the Temporary Import Scheme under Singapore Customs or the relevant Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) schemes:
To account for the entry of your goods, please follow the steps below to obtain the relevant import permits and authorisation (if the goods are subject to control) from the relevant Competent Authorities.
Step 1: Register for Unique Entity Number and Activate Customs Account
An entity that intends to:
Engage in import or export activities in Singapore, or
Obtain import, export and transhipment permits or certificates
will need to:
Register with the Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) or the relevant Unique Entity Number (UEN) issuance agency to obtain a UEN; and
Step 2: Check if Your Goods are Controlled
Do check if the goods you intend to import are controlled goods or goods subject to restrictions by Competent Authorities (CAs) in Singapore.
You may search using the description of the goods, Harmonised System (HS) code or CA product code. If the item is subject to control, the name of the CA will be indicated next to its HS code. You may check directly with the respective CAs on their licensing requirements.
If you require advice on the full 8-digit HS code of the product, you may apply for an official classification ruling at a fee of S$75 per product. Please note our classification rulings are only applicable for use within Singapore.
Step 3: Apply for Inter-Bank GIRO
You or your Declaring Agent (DA) must maintain an Inter-Bank GIRO (IBG) with Singapore Customs to make payment of duties, taxes, fees, penalties and other charges on services offered by Singapore Custom from your bank account to Singapore Customs directly.
Mail the completed Application for Inter-Bank GIRO form to Singapore Customs’ address as indicated in the form.
You may authorise your DA to use your IBG for the payment of duties and GST for your customs permit one day after the approval of your IBG application. If you do not maintain an IBG with Singapore Customs, the duties and GST will be deducted from your DA’s IBG
Step 4: Furnish Security
You are required to furnish security for transactions involving dutiable goods, temporary import of goods for approved purposes, and for the operation of licensed premises such as licensed warehouses and excise factories.
The security furnished should be in the form of a Banker’s Guarantee, Finance Company Guarantee or an Insurance Bond.
Please see security lodgement for more information.
Step 5: Obtain Customs Import Permit
You may:
Appoint a DA to obtain customs permits on your behalf; or
Obtain customs permits for your own or on behalf of your clients. To do so, you will need to register as a DA and apply for a TradeNet user ID.
All permit applications must be submitted via TradeNet, which is accessible through:
TradeNet front-end software from an approved software vendor; or
Please refer to Permits, Documentation and Other Fees for more information. DAs may charge additional service fees. You may wish to check with your appointed DA on the charges involved.
Step 6: Prepare Documents for Cargo Clearance
Approved permits applications are issued with a validity period. You should ensure the validity of the permit presented for goods clearance. For imports of containerised cargo, the container number and shipper seal number are required when applying for a permit.
a) Documents Required for Containerised Cargo
For import of containerised cargo by sea, you are not required to present the printed copy of the customs permit and supporting documents to the checkpoint officers at the entry points.
For import of containerised cargo by air or land, you are required to produce the customs permit and supporting documents such as invoice, packing list and Bill of Lading/Air Waybill, to the checkpoint officers for verification.
An example of conditions in the customs permit indicating this requirement:
Specific Customs clearance and endorsement requirements for different permit codes (A1, A3, and H1) at various Singaporean checkpoints.
A1 | The goods and this permit with invoices, BL/AWB, etc must be produced for Customs clearance/ endorsement at a Free Trade Zone “In” Gate. |
A3 | The goods must be produced with this permit, invoices, BL/AWB, etc for Customs endorsement at an Airport Customs checkpoint or designated Customs office or station as required. |
H1 | The goods and this permit with invoices, BL/AWB, etc must be produced for Customs clearance at Woodlands Checkpoint / Tuas Checkpoint. |
Please note partial clearance is not allowed for goods brought in via Woodlands and Tuas checkpoints.
b) Documents Required for Conventional Cargo
For conventional cargo, please present the goods, printed copy of the customs permit, and supporting documents such as invoice, packing list and Bill of Lading/Air Waybill, to the checkpoint officers at the time of cargo clearance for verification.
An example of conditions in the customs permit indicating this requirement.
A1 | The goods and this permit with invoices, BL/AWB, etc must be produced for Customs clearance/ endorsement at a Free Trade Zone “In” Gate. |
A3 | The goods must be produced with this permit, invoices, BL/AWB, etc for Customs endorsement at an Airport Customs checkpoint or designated Customs office or station as required. |
H1 | The goods and this permit with invoices, BL/AWB, etc must be produced for Customs clearance at Woodlands Checkpoint / Tuas Checkpoint. |
For a consignment which requires partial clearance, the same customs permit should be presented each time for endorsement till the whole consignment is completely cleared.
Please note partial clearance is not allowed for goods brought in via Woodlands and Tuas checkpoints.
c) Documents Required for Cargo Clearance of Air Imports Granted GST Relief at Changi Airfreight Centre Checkpoint
GST relief and permit waiver is granted on non-controlled and non-dutiable air imports imported by post or air with a total Cost, Insurance and Freight (CIF) value not exceeding S$400.00. To facilitate the cargo clearance of such air courier parcels/consignments at the Changi Airfreight Centre Checkpoint, freight forwarders/handling agents are allowed to use a summary list, together with the invoice and House Airway Bill (HAWB)/consignment note for each parcel/consignment. You may wish to find out more about the Documents Required for Clearance of Goods.
Step 7: Retain your Trade Documents
Generally, you are required to retain the relevant supporting documents relating to the purchase, import, sale or export of the goods for a period of 5 years from the date of the permit application approval.
These documents can be stored as physical hardcopies or as images. You are required to produce these supporting documents to Singapore Customs upon request.
